PPC or Pay Per Click: What it is, Advantages and Examples
PPC or Pay Per Click is the advertising modality on which most Internet campaigns are based, such as Google Advertising. For advertisers, this model was a real revolution, since until then they had to “shoot blindly”, investing budget in campaigns whose results could not be measured with certainty.
In short, PPC is a basic concept to understand digital marketing. But do you know exactly what it consists of, what advantages it has, and how it is applied? Let’s take a look!
What is PPC?
PPC or pay-per-click is a digital advertising model in which the advertiser pays an amount (fixed or determined by auction) every time a user clicks on one of their ads to visit their website. The idea of a pay-per-click campaign is to “buy visits” to a certain site, usually with the idea of generating a certain action in users (registering or buying a product, for example).
Although PPC is a very common option, it is not the only possible payment model for running online campaigns. Therefore, it is convenient to distinguish it from others, such as:
- PPM (pay per thousand): The advertiser pays a fixed amount for every thousand impressions, that is, each time the ad is shown a thousand times to users. Keep in mind that with this model, we don’t know how much we are going to pay for each visit, since it is possible that those thousand impressions generate many clicks, few or none.
- PPA (pay-per-acquisition): The advertiser pays for each time the user performs a certain action, for example, downloading an app. The link between cost and targets is therefore even more evident than in the case of PPC.
Some key concepts to understand PPC
CPC or cost per click
The CPC is the price the advertiser pays for each click on their ad. Here, a fixed price can be agreed for each click or determined by auction. In the second case, the advertiser sets a maximum bid or price that they are willing to pay for each click. The system compares the ad with similar ads based on their quality and the price they’re willing to pay, and shows the winning ad first.

CTR
The CTR (“Click through rate” or click-through rate) is the percentage of users who click on an ad out of the total number of users who have seen it. In general, the better an ad is, the higher its CTR will be.
In some PPC systems, CTR is a determining metric for setting the price of an ad, as the system “rewards” ads that have higher quality and, therefore, higher CTR.

Impression
We call each of the views that an ad receives, whether the user clicks on it or not, an “impression”.
Segmentation
With Internet Advertising, we have a great deal of control over the audience our ads are targeting. Can segment the audience that will see our PPC campaigns depending on many factors: age, gender, location, interests, behaviours… Each pay-per-click platform offers different options that we can combine to achieve a high level of accuracy. Thus, we make sure that we only pay for clicks from users who have a good chance of becoming our customers.
Landing page
The landing page is the site to which the user is directed after clicking on our ad. It depends on whether they end up becoming a customer or leave within a few seconds, so it is very important that it is well optimized.
The main characteristics of a good landing page are clarity, simplicity, and relevance to the ad.
Conversion
Conversion is probably the most important metric in a PPC campaign, as it measures the performance of our ad in economic terms. We call each of the purchases made by a user after clicking on an ad a “conversion”. The conversion rate is the percentage of users who convert compared to the number of users who click.
Conversion Rate = Number of Conversions/Website Visits
Frequency
The number of times each ad is shown to a specific user during a given time period. To calculate it, we need to divide the number of impressions by the number of unique users.
Frequency Number of impressions/ Number of unique users
It is common for a user to receive several hits from the same campaign, and it can be a good idea to make sure that they have seen us. But we must avoid falling into excess, as we can end up generating rejection and a feeling of spam and achieving an effect contrary to the desired one.
Advantages of PPC
- You only pay for the visits you receive. In other advertising systems, the advertiser pays an amount to show the ad, but they have no guarantee that it is generating results. With pay-per-click, on the other hand, there is a direct link between cost and visits.
- You have a lot of information about how your ad is performing. Pay-per-click platforms provide the advertiser with complete information about what is happening with the ad, including the number of impressions, clicks, CTR, and conversions.
- Good optimization possibilities. With all this data, it’s very easy to know if an ad is working or not and correct course in real time. In fact, the best strategy is to create several variants of each ad and compare them with each other to see which ones work best. In this way, we can get our advertising to have better and better results.
- Ads only reach the right audience. Thanks to the multiple targeting options, we don’t waste a single click, as only the users we are most interested in will see the ad. In turn, this improves ad results, as a user who is part of the target audience is more likely to click. And as we have seen, the higher the click-through rate, the lower the cost of the ad.
- You can control your budget precisely. PPC systems allow you to set a maximum budget per day, and in some, you can start with as little as one euro. This means that they can be adapted to advertisers of all sizes and that you can control in advance how much you are going to spend on each campaign.
- You can decide where and at what times your ad will show. Within the pay-per-click model, you can show your ads on many different platforms and locations (we’ll show you some examples in the next section) and select the ones that interest you most. Some sites also allow you to choose the days and times when your ads will show.
- You will get more positioning and visibility. Thanks to PPC, you will be able to show your ads on some of the most visited sites by users, such as search engines, social networks, or the most famous web portals.
Examples: Where is pay-per-click used?
PPC is a paid model, not a specific site or location; therefore, you have many options when deciding where you want to show your ads. We show you the main ones.
PPC ads on search engines
Search engine advertising, also known as SEM, allows you to show ads to users based on the keywords they have entered in their search (for example, “car rental in Madrid”). Major search engines, such as Google and Bing, use a PPC-based auction model.
For advertisers, search advertising offers two major advantages:
- It is highly visible, as the ads appear on the first page of search results. Managing to position your website there organically can take you years of work, but thanks to ads, you can be present for a very reduced price.
- It is very effective, as it is aimed at users who are looking to satisfy a certain need, and that has to do with our products or services.
PPC ads on social media
Major social media advertising solutions, such as Facebook Ads or Instagram Ads, offer pay-per-click options.
These types of ads are located within the user’s experience of the social network, either in its latest news section or in a side column. One of its main advantages is that it allows us to take advantage of the information that the social network has about the user, so that we can launch highly segmented PPC ads (for example, “married men who have recently moved to X”).
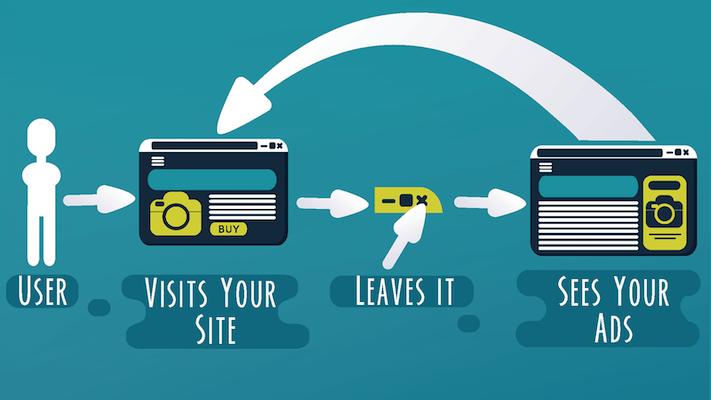
Display PPC ads
Finally, PPC is also the bread and butter of display advertising campaigns, which display banner ads on websites related to the brand’s products and services or the interests of its target audience.
These types of campaigns can be very effective if they are well used, but you have to be careful to avoid falling into intrusive advertising. It’s also worth bearing in mind that CTRs tend to be much lower than other types of ads, so you’ll need to have a larger audience.